CLINICAL APPEARANCE OF THE PATIENT IN DKA - QUIZ QUESTIONS
Clinical appearance of the patient in DKA
picture of a patient in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). His blood
glucose was 600. Tom has an altered level of consciousness (LOC).
He also has hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose).
Please watch the video below:
Dehydration
of care like ICU.
Patient education
Frequent monitoring of blood glucose, Insulin IV, Potassium
replacements are included in the management.
Learn more:
1) What are some of the signs of a patient in DKA?
2) How is DKA managed?
3) What is another name for hyperglycemia?
Sessions 41- Diabetic and seizure patients
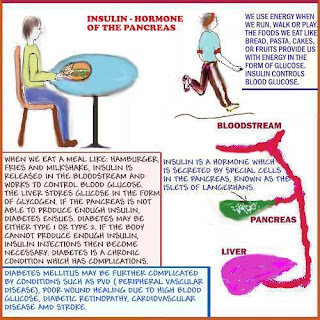
Insulin is a hormone which is produced
in the pancreas by special glands known
as the Islets of Langerhans.
When we eat a meal like hamburger, fries and milkshake,
Insulin is released in the blood stream to control blood glucose.
The liver stores glucose in the form of glycogen. If the pancreas
is not able to produce insulin, diabetes ensues.
Diabetes Mellitus may be Type 1 or Type 2.
Diabetic complications
Scenario: Sara is a young adult who was diagnosed
with Type 2 diabetes, about a year ago. She has now
been admitted for visual problems.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Sara's eye exam reveals Diabetic Retinopathy. This
condition affects the blood vessels in the eye. Poor
vision and possible blindness may result from leaking
and weakening of the blood vessels.
Diabetic Nephropathy
This condition may further complicated diabetes.
Poor renal function and possibly renal failure may
result. Hemodialysis then becomes necessary.
The consequences of poor circulation
is also at risk for stroke or renal failure.
The diabetetic patient is also at risk for stroke.




Comments
Post a Comment