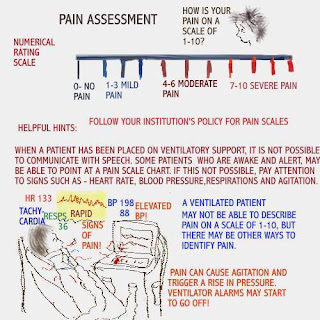
PAIN ASSESSMENT OF THE PATIENT ON MECHANICAL VENTILATION
it is not possible to communicate with speech. Some
patients who are awake and alert may be able to point
at a pain scale chart. If this is not possible, pay attention
to signs such as: heart rate, blood pressure, respirations,
and agitation.
The patient on mechanical ventilation is unable to speak,
because there is an endotracheal tube in the airway. Signs
of pain may manifest by: agitation, pressure alarms on the
ventilator going off, rapid heart rate and more.
Pain is assessed by using a scale of 1-10, ten being the worst.
Common scale ratings are as follows:
- 0: No pain
- 1-3: Mild pain
- 4-6: Moderate pain
- 7-10: Severe pain
Learn more about : ARDS, DVT and PE
Scenario: Nick was admitted to the hospital with a history
of lung cancer. He calls the nurse with complaints of a sudden
onset of shortness of breath and sharp chest pain.
of lung cancer. He calls the nurse with complaints of a sudden
onset of shortness of breath and sharp chest pain.
Nick's oxygen saturation was checked using the pulse oximeter.
It was low and the nurse gave him oxygen via nasal prongs.
It was low and the nurse gave him oxygen via nasal prongs.
The nurse documents and notifies the doctor of her findings.
What is a Pulse Oximeter?
A pulse oximeter is a device that is used to detect the oxygen
saturation in the blood. It is generally applied to the finger
and a patient's oxygen saturation is shown. It is a painless
and effective test.
What is a Pulse Oximeter?
A pulse oximeter is a device that is used to detect the oxygen
saturation in the blood. It is generally applied to the finger
and a patient's oxygen saturation is shown. It is a painless
and effective test.




Comments
Post a Comment