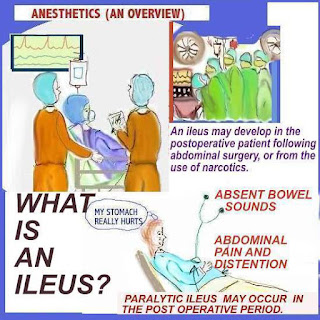
QUICK QUESTION - WHAT IS AN ILEUS?
An ileus may develop in the postoperative patient,
following abdominal surgery. It may also occur from
the use of narcotics.

the use of narcotics.
The warning signs include: abdominal pain, distention
and absent bowel sounds.
and absent bowel sounds.

Learn more about: PACU and Quiz questions
Learn more about: Organizational skills



Comments
Post a Comment